Pigment dispersion is a critical yet often underestimated challenge in masterbatch production. Poor dispersion can lead to issues like uneven color distribution, clogged filters, fiber breaks in spun fibers, and weak welded seams. These problems not only affect product quality but also increase production costs due to higher pigment consumption and machinery downtime. Below is a concise guide to tackle these challenges effectively, based on industry practices:
1. Optimize Pigment Selection
Choose Compatible Pigments: Select pigments that are compatible with the polymer base (e.g., PE, PP, PET) to ensure proper wetting and dispersion.
Particle Size and Surface Treatment: Use pigments with smaller particle sizes for better dispersion. Surface-treated pigments (e.g., with dispersants or coatings) help reduce agglomeration and improve flow properties.
Pigment Loading: Avoid exceeding the recommended pigment load (typically 20-40% for organic pigments, 50-80% for inorganic). Overloading can cause agglomeration and poor dispersion.
2. Enhance Mixing and Compounding
High-Shear Mixing: Use twin-screw extruders or high-shear mixers to break down pigment agglomerates. Adjust screw configuration (e.g., kneading blocks) to optimize shear and enhance dispersion.
Pre-Mixing: Blend pigments with dispersants or carrier resins before extrusion to improve initial wetting and reduce clumping.
Temperature Control: Maintain optimal melt temperatures to avoid pigment degradation or viscosity issues. For heat-sensitive pigments (e.g., certain organic pigments), keep temperatures below their degradation thresholds.
3. Use Dispersing Agents
Additives: Incorporate dispersing agents like waxes, stearates, or polymeric dispersants (e.g., polyethylene wax, EVA-based additives) to reduce viscosity and improve pigment wetting.
Dosage: Typically, use 1-5% dispersant by weight, depending on pigment type and loading. Overuse can negatively affect mechanical properties and may cause blooming (a surface appearance issue).
Novel Hyperdispersant for Masterbatch: SILIKE SILIMER Series – High-performance processing aids and dispersing agents.
SILIKE SILIMER Series Processing Aids and Dispersing Agents are next-generation silicone-based waxes(also named Silicone Hyperdispersants) engineered to deliver superior pigment and filler dispersion in masterbatch production. It’s ideal for color concentrates, filled compounds, engineering plastics, and demanding dispersion processes. These hyperdispersants enhance thermal stability, rheology, and cost efficiency while eliminating migration issues common with traditional additives (e.g., waxes, amides, esters).
Unlock Superior Pigment Performance with SILIKE SILIMER Series Silicone Hyperdispersants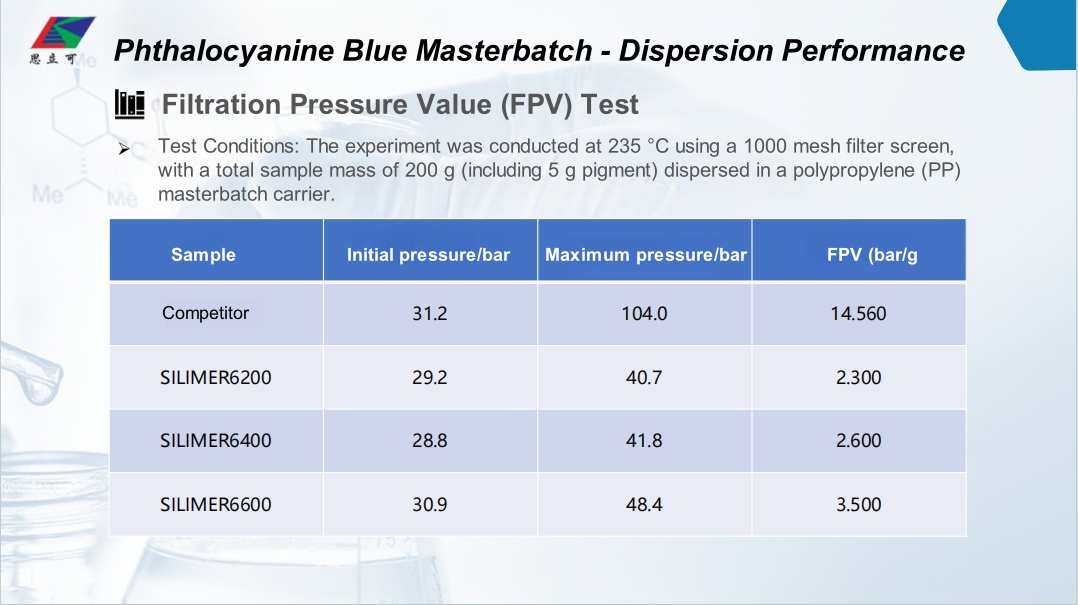
Maximize Efficiency in Pigment Concentrates for a Variety of Materials:
→ For Polyolefins: Elevate Your Pigment Quality
• Enhanced Pigment Wetting: Achieve smoother, more vibrant pigments with optimized interaction.
• Improved Dispersion: Prevent pigment clumping, ensuring uniform color and consistency.
• Viscosity Reduction: Streamline production with smoother flows for better processing.
• Higher Output: Increase production capacity without compromising quality.
• Increased Pigment Concentration: Achieve richer hues with less material, reducing costs.
→ For Engineering Plastics and Polymers: Boost Quality and Efficiency
• Improved Surface Gloss: Achieve a superior, glossy finish on your products.
• Better Mold Release: Ensure smoother manufacturing processes and reduce defects.
• Viscosity Reduction: Enhance processing and reduce energy consumption.
• Higher Production Output: Streamline your production line for higher throughput.
• Reduced Pigment Shear: Preserve the integrity of pigments for vibrant, lasting colors.
• Superior Dispersion: Maximize consistency in color and material performance.
Why Choose SILIKE’s Silicone Hyperdispersants?
• Cost-Effective: Improve efficiency and reduce material waste.
• Eco-Friendly: Achieve sustainability goals with optimized production processes.
• Versatile Application: Suitable for a wide range of polymers and industries.
4. Adjust Processing Parameters
Screw Speed: Increase screw speed (typically 200-500 rpm) to enhance shear and dispersion. Avoid excessive speeds, as this can lead to thermal degradation.
Residence Time: Optimize residence time in the extruder (typically 30-60 seconds) to ensure thorough mixing without overheating.
Filtration: Use screen packs (e.g., 100-200 mesh) to remove undispersed particles and ensure uniform masterbatch quality.
5. Address Equipment and Maintenance Issues
Clean Equipment: Regularly clean extruders, screws, and dies to prevent contamination or the buildup of degraded material that affects dispersion.
Wear Check: Inspect screws and barrels for wear, as worn equipment reduces shear efficiency and leads to poor dispersion.
Feeding Accuracy: Use gravimetric feeders for precise pigment and resin dosing, ensuring consistency in pigment dispersion.
Post time: May-29-2025






